The Evolution of HTML: A Journey Through the Digital Ages
HTML, or HyperText Markup Language, is largely responsible for the existence of the internet as we know it today.
This essential technology has shaped how we generate and engage with online content, serving as the foundation for web development.
Let's explore the interesting development of HTML over the years and take a trip down memory lane.
The Humble Beginnings


The history of HTML starts with a man by the name of Tim Berners-Lee in the late 1980s. A system that would make it simple for scientists to share documents online was Berners-Lee's ambition while he was employed at CERN (the European Organisation for Nuclear Research). In 1991, HTML was developed as a result of this concept.
HTML 1.0, the original version of the language, was extremely simple. It had a limited number of elements, such as lists, headings, paragraphs, and links. HTML 1.0, for all its simplicity, set the foundation for a world that was more open and connected.
The Growth Spurt
The need for increasingly intricate web sites increased along with the adoption of the internet. As a result, HTML 2.0 was released in 1995.
By adding new components like tables and forms, this version improved upon the original and made more structured and interactive content possible.
But HTML 3.2, released in 1997, was the true game-changer. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) created this version, which reflected the increasing complexity of web design by supporting elements like applets and complicated tables.
The Rise of Modern Web Design
The 1997 release of HTML 4.0 was a critical turning point. It brought JavaScript and cascading style sheets (CSS), two innovations that completely changed online design. Developers could more easily create aesthetically pleasing websites by separating content from design using CSS. JavaScript introduced interactivity to websites by enabling them to react dynamically to user input.
XHTML, or Extensible Hypertext Markup Language, also came into being around this time. The goal of XHTML was to standardize and give HTML the rigor of XML, resulting in well-formatted online pages. It didn't take off as quickly as expected, though, because a lot of developers thought it was too rigid.
The HTML5 Revolution
After years of development and cooperation, HTML5 was finally published in 2014, marking the next significant advancement. In order to meet the demands of contemporary web applications, HTML5 was created. With the introduction of numerous new elements and APIs, including `<video>}, {<audio>}, and {<canvas>}, native multimedia support was made possible without the use of third-party plugins.
Semantic elements like `<article>}, `<section>}, and `<nav>} were also introduced by HTML5, improving the readability and accessibility of web pages. It also enhanced support for geolocation, real-time communication, and offline storage, opening the door for more potent web apps.
Beyond HTML5
With HTML5, the world of HTML continued to change. New features and enhancements to HTML are constantly being added as part of its ongoing development, also known as HTML5.1 and HTML5.2. These include improved privacy and security awareness, improved integration with contemporary APIs, and improvements for responsive site design.
For example, HTML5.1, which was made available in 2016, featured enhancements including the `picture} element for responsive pictures and enhanced form controls. With the release of HTML5.2 in 2017, new capabilities were added, such as the `dialogue` element for modal dialogue creation and more security measures to safeguard user data.
HTML and Web Standards
The standardization of HTML has been an important part of its evolution. The development and upkeep of HTML standards have been greatly aided by groups like the Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). These guidelines guarantee that web information is readable and consistent across various browsers and gadgets.
The versatility and endurance of HTML have been largely attributed to the collaborative character of these organizations, which solicit feedback from developers, businesses, and users globally.
HTML and Accessibility
The evolution of HTML has focused heavily on accessibility, which has been one of its most significant features. Ensuring the accessibility of web material for individuals with impairments is a top responsibility. To help make web content more accessible to everyone, including those using screen readers and other assistive technology, features like ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) attributes have been incorporated into HTML.
HTML and Mobile Web
HTML had to change to accommodate the mobile web with the introduction of smartphones and tablets. The ability of online pages to smoothly adapt to varying screen sizes is made possible by responsive design, which has become an essential component of web development. The `viewport` meta tag and the previously mentioned `picture` element for responsive pictures are two of the elements that HTML5 brought that help responsive design.
HTML Versions and Key Changes

A More Detailed Look at Key Versions
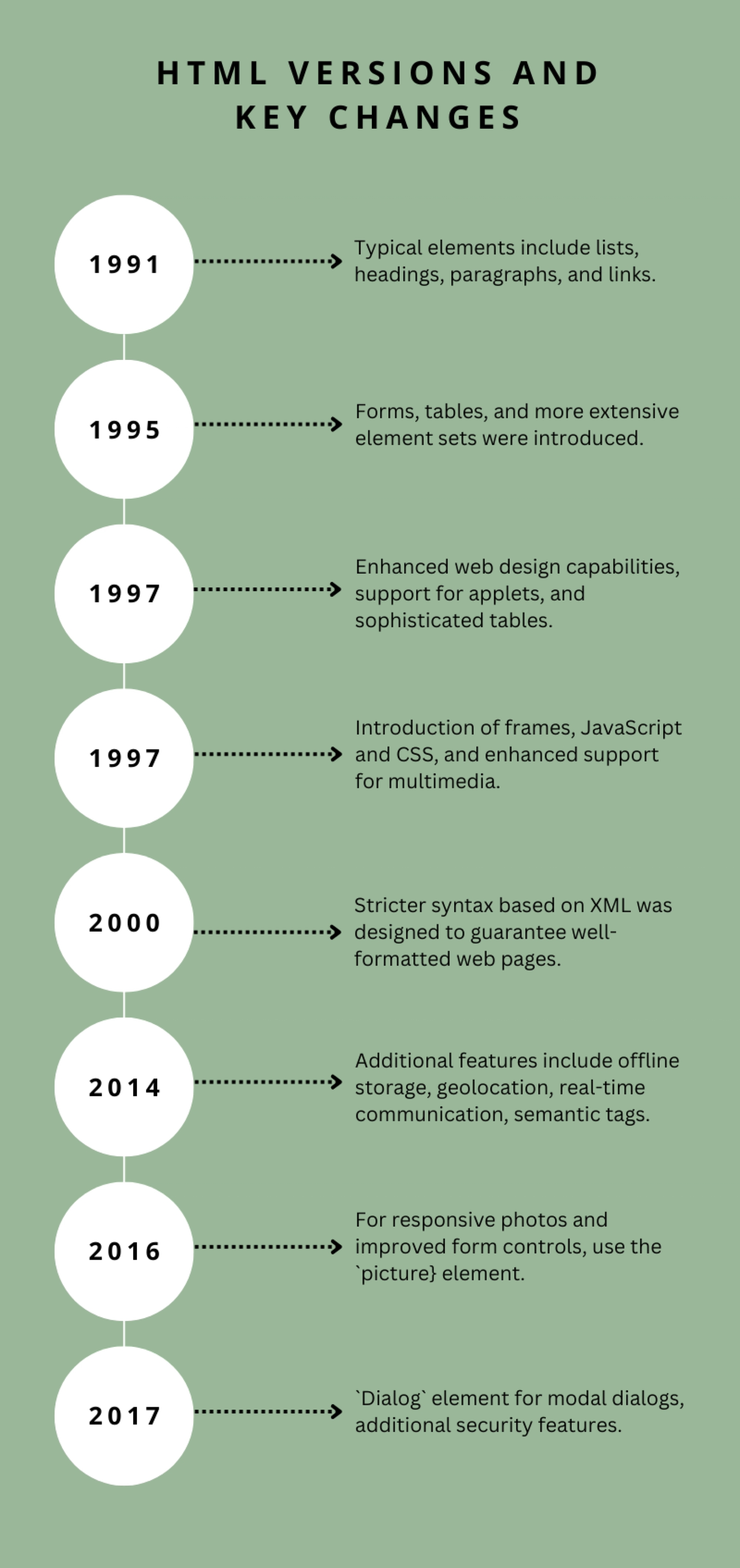
# HTML 1.0
- Release Year: 1991
- Key Features: `<p> for paragraphs, <a> for links, <ul> / <ol> for lists, and <h1> to <h6> for headings comprised the basic structure of web pages.
- Impact: laid the groundwork for the World Wide Web by making it possible to share and link documents easily.
# HTML 2.0
- Release Year: 1995
- Key Features: Support for forms <form> was added, enabling user input; tables <table> were introduced, enhancing data presentation.
- Impact: made it possible for web sites to be more structured and dynamic, which was crucial for early e-commerce and data collection.
# HTML 3.2
- Release Year: 1997
- Key Features: Improved layout features like <div> presentational attributes like <font> applet support, and complicated tables are all included.
- Impact: Permitted the creation of more intricate and eye-catching websites in response to user expectations that are developing.
# HTML 4.0
- Release Year: 1997
- Key Features: Introduction of JavaScript for client-side scripting, frames for segmenting browser windows into different portions, and CSS for improving the separation of content and design.
- - Impact: Strengthened the structure of web papers and enabled more dynamic and interactive content, revolutionizing web design.
# XHTML 1.0
- Release Year: 2000
- Key Features: More stringent guidelines for properly formatted papers and an XML-based syntax.
- Impact: aimed to improve consistency and compatibility with XML tools by introducing more discipline into HTML writing.
# HTML5
- Release Year: 2014
- Key Features: APIs for offline storage, geolocation, and real-time communication; canvas for graphic sketching; new multimedia elements like {<video>} and `<audio>}; semantic elements like <article>, <section>, <nav>.
- Impact: Improved mobile web experience; enabled developers to create richer, more dynamic online applications without depending on third-party plugins like Flash.
# HTML5.1 and HTML5.2
- Release Years: 2016 and 2017
- Key Features: Incremental enhancements like the `picture` element for responsive pictures, enhanced form controls (`<input type="date">`), and the `dialogue` element for modal dialogues; new security features.
- Impact: HTML5 has been further refined and improved, meeting new requirements for web development and improving user experience.
The Role of Browsers
Web browsers have been essential to the development of HTML. Among the earliest browsers to render HTML content were the early versions of Netscape Navigator and Mosaic. Browsers changed along with HTML, with each new version supporting more functionalities.
In addition to rendering HTML, modern browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Safari also support a variety of web standards, guaranteeing that websites work and seem the same on many platforms. Competition amongst browser developers has sparked innovation, improving security, performance, and user experience.
The Impact of HTML on Web Development
Web development has been greatly impacted by the growth of HTML:
- Accessibility: Thanks to features like ARIA, individuals with disabilities can now access web content more easily.
- Interactivity: HTML has made it possible for extremely interactive online applications with the advent of JavaScript and subsequent improvements.
- Multimedia: The native support of audio and video components has improved the integration and accessibility of multimedia material.
- Semantic Web: By incorporating semantic components, web material is better understood by assistive technologies and search engines alike.
Looking Ahead
As we look to the future, HTML continues to evolve. The ongoing development focuses on improving accessibility, performance, and security. Emerging technologies like WebAssembly are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible on the web, promising faster and more efficient web applications.
In conclusion, the history of HTML is a testament to the rapid evolution of technology and the web. From its modest beginnings as a simple markup language to its current role as a cornerstone of modern web development, HTML has continuously adapted to meet the changing needs of the digital age. As we continue to innovate and explore new possibilities, one thing is certain: HTML will remain at the heart of our online experiences for years to come.
The next time you explore the internet, stop and consider HTML's amazing journey and the many hours of labor that have gone into creating a more dynamic, colorful, and connected internet.
